Inside The Lab HarfangLab's tech Blog
Loading...

Analysis of the APT31 indictment
Identifier: TRR240401 On March 25, 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice (DoJ) released an indictment of seven hackers associated with APT31, a “hacking group in support of China’s Ministry of State Security” (MSS) which has been active for 14 years.…

Raspberry Robin and its new anti-emulation trick
Reported for the first time by Red Canary in 2021, Raspberry Robin was the 9th most prevalent threat in 2023 according to their “2024 Threat Detection Report”. Starting as a worm, it evolved to become an initial access broker for…

A comprehensive analysis of I-Soon’s commercial offering
Identifier: TRR240301. Key Findings I-Soon’s commercial offering reveals that their main issue is processing collected data, not breaching their targets in the first place. Their products leverage deep learning to help them sort and classify stolen documents. The company appears…

Hamas-linked SameCoin campaign malware analysis
Identifier: TRR240201. Summary Following an X post by IntezerLab about an attack campaign that they dubbed “SameCoin”, we analyzed the samples they discovered and found a few identical variants. The infection vector appears to be an email impersonating the Israeli…

Compromised routers are still leveraged as malicious infrastructure to target government organizations in Europe and Caucasus
Identifier: TRR240101. On 2023-12-28, the Ukrainian government computer emergency and incident response team (CERT-UA) described a malicious espionage campaign that targeted government organizations in Ukraine. CERT-UA attributed the campaign to the APT28 threat-actor (aka Sofacy, Fancy Bear, etc.). The malicious…

2024 Threatscape report
As we step into 2024, we anticipate a year that is poised to set several significant precedents. In this blogpost, we provide our Threatscape report, presenting our predictions for the global threats that lie ahead in the upcoming year. These…
An introduction to reverse engineering .NET AOT applications
About a month ago, we started seeing reports on activities from DuckTail , a cybercrime outfit reportedly based in Vietnam. Detonating one of the samples, we observed that a new account was being created on the analysis machine, followed by…

Machine Learning to identify malicious strings in a file
Why bother with strings? When analyzing a new sample found “inthewild”, it may make sense to extract the strings within it to identify IP addresses, domains, log files or C&C server signatures. For example, if an Artificial Intelligence model such…

How many slices of pizza do you need to appear in MITRE?
“We don’t see you in MITRE.” “Your solution hasn’t even been benchmarked, so how can anyone know what you’re REALLY worth?” “Anyway, it’s impossible for a French player to be as good as the Americans…” … okay, okay, that’s enough…
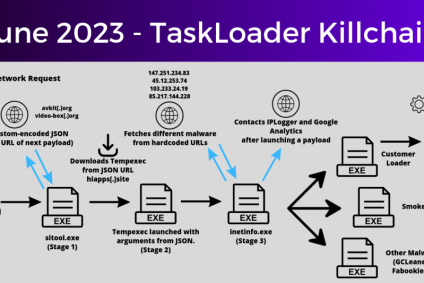
Taskloader at the root of a Pay-per-Install infection chain
In June 2023, we’ve observed multiple alerts that seemingly came from different sources. A quick search through our telemetry allowed us to identify multiple infected machines across our clients. Although they would sometimes present different behaviour, the initial infection vector…
Simulate the activity of a brute-force attack
For the purpose of testing an unsupervised anomaly detection algorithm, we need a dataset with both benign and malicious authentication activities. We already have access to benign data, but we lack malicious attack events.</p> The question we will try to…
